Rotate / Zoom 
Ctrl + Shift + Z
The command to open the Rotate/Zoom dialog can be found in the
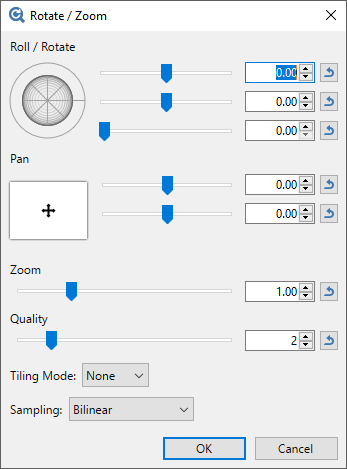
Roll / Rotate
Outer Ring
The active layer can be rotated about the Z axis by clicking and dragging dragging the outer ring of the
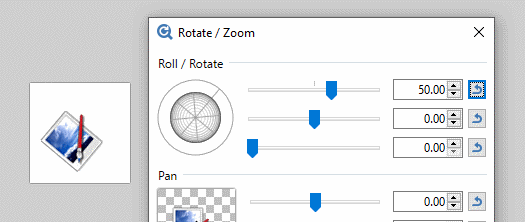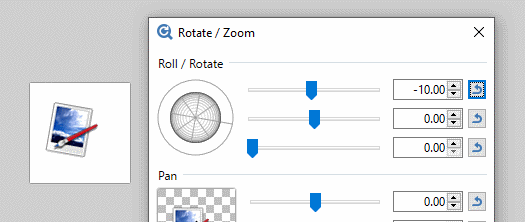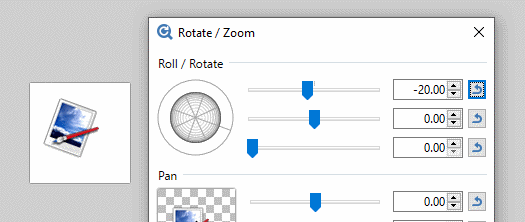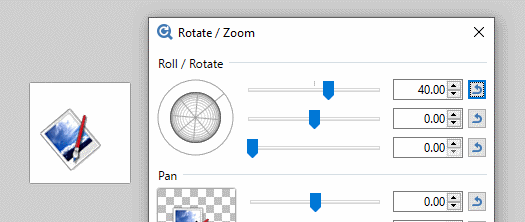
The Z axis is aligned through the center of the Roll control "globe" and the reticle. If the Roll control is realigned so the reticle is pointing South East, the Z axis will also be aligned to the South East. Rotations using the outer ring will appear to be centered about this axis.
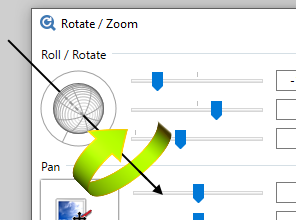
Holding
Roll Control
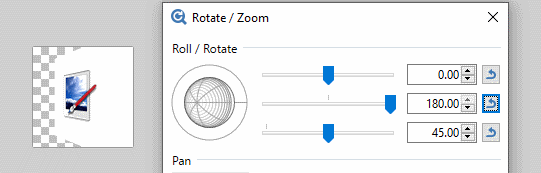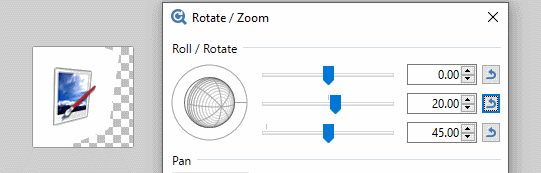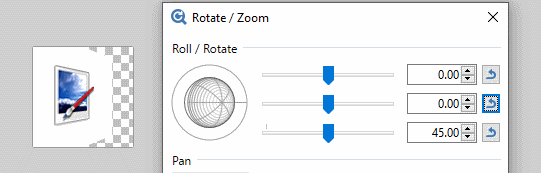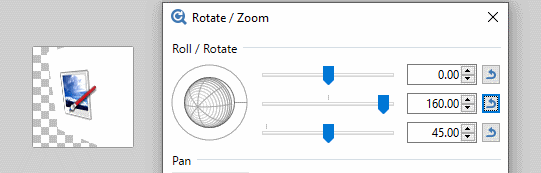
The Center of the Roll/Rotate control allows rotations simultaneously about the X and Y axes. The control can be clicked and dragged as can sliders two and three respectively. Values can also be typed directly into the numeric input boxes.
The third slider is perhaps the easiest understood. It controls the apparent tilt of the image from zero (front on) to 90 degrees (side on)
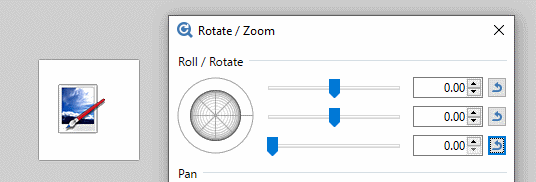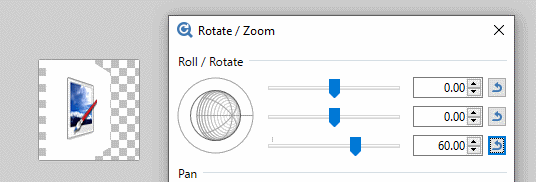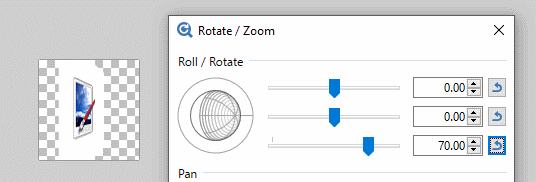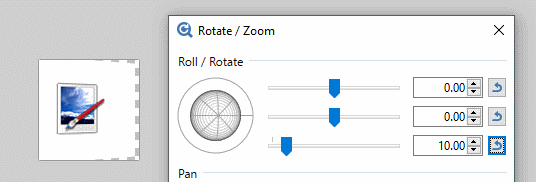
The second slider determines which compass direction the reticle faces. Zero is due East, 90 degrees South, 180 degrees (both + and -) West and -90 degrees faces North. The action of the second slider is most obvious when the third slider is non-zero.
Pan
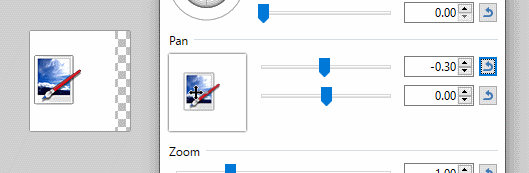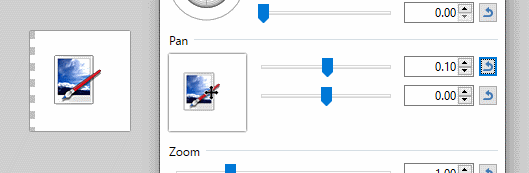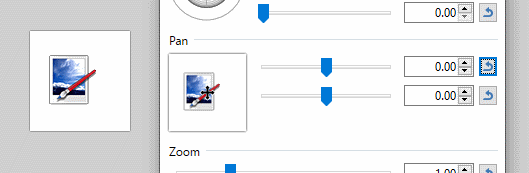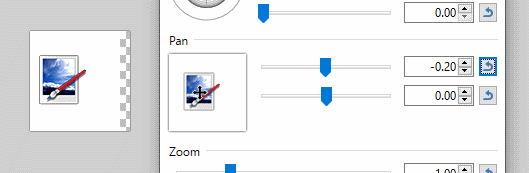
Panning is the action of sliding the image in the same plane as the rest of the layer. Click and drag the control or use the sliders to move the layer around the canvas.
The upper Pan slider controls movement horizontally. The lower pan slider controls movement vertically.
Zoom
This control expands or contracts the area being manipulated. Higher zoom settings increase the size of the area. Smaller values shrink the contents.
Quality
This control determines the output fidelity or detail which is retained during manipulation. Higher quality settings will use more samples from the image, effectively antialiasing it. Low quality settings will use fewer samples and can result in aliasing or pixelation artifacts (especially when combined with Nearest Neighbor sampling mode).
Tiling
The three
-
None - any portion of the layer not filled by the image under transformation will be rendered transparent. The image will not be tiled or repeated.

Rotate Zoom with tiling mode: None
-
Repeat - any portion of the layer not filled by the region under transformation will be filled with a repeating pattern of the transformed image.

Rotate Zoom with Repeat tiling mode
-
Mirror - as for Repeat except each iteration of the pattern is a mirror image of the last.

Rotate Zoom with Mirror tiling mode
Sampling
When rotating or resizing, there are two resampling modes available: Bilinear and Nearest Neighbor.
Nearest Neighbor will produce a more pixelated or blocky result. Bilinear will produce smoother results.
Combine the sampling mode with the Quality setting to fine-tune the quality or detail of the image manipulation.
Usage
Using the Rotate/Zoom controls allows an image to be tilted and transformed as if it were at an angle to the viewer. It is relatively easy to create the illusion of depth or perspective using these tools.
Example