Blur Effects
This sub-menu contains ten effects which are used to blur sections of an image.
Note
Looking for Unfocus? In Paint.NET 5.0+ the Bokeh Blur effect has replaced Unfocus (Bokeh even shows the same icon Unfocus used to have). Bokeh is able to replicate the transformation Unfocus used to produce, while allowing finer control of the effect via the Radius, Gamma and Quality controls.
The following image will be used to demonstrate the

Note
The examples on this page show the effects being applied to an entire image. It is easy to restrict the adjustment to a sub-section of the image simply by making a selection. If a selection is active when the effect is run, it will only be applied to the selected region. Areas outside of the active selection will remain unchanged.
Tip
The controls shown in the effect dialogs operate in much the same way; drag the indicator left, right or in a circular motion (for an angle control).
Typing in a numeric value in the text box or using the up/down arrows beside the text box also changes the current value.
The keyboard arrow keys can be used to alter the value of a control once it has the focus.
Multiple controls can be used in isolation or combination. If more than one is altered, the cumulative effect will be shown.
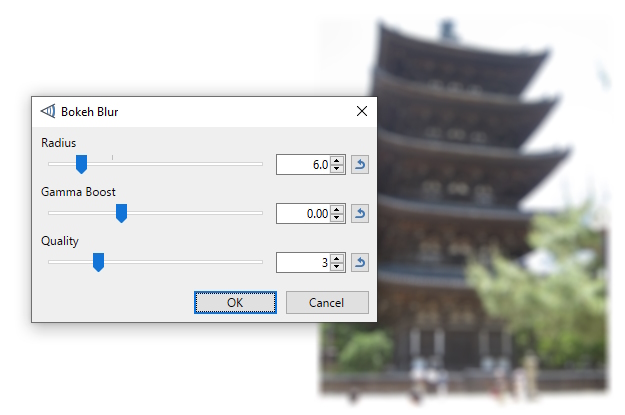
 Bokeh Blur
Bokeh Blur
Applies the BOKEH effect to the source image.
Bokeh is most commonly seen as the blurred effect in the out-of-focus portion of a photograph taken with a narrow depth of field.
The result averages color in the surrounding circular area.
Applying the effect to parts of an image draws the viewer's attention to the unblurred subject.
The
Example - Effects > Blurs > Bokeh Blur
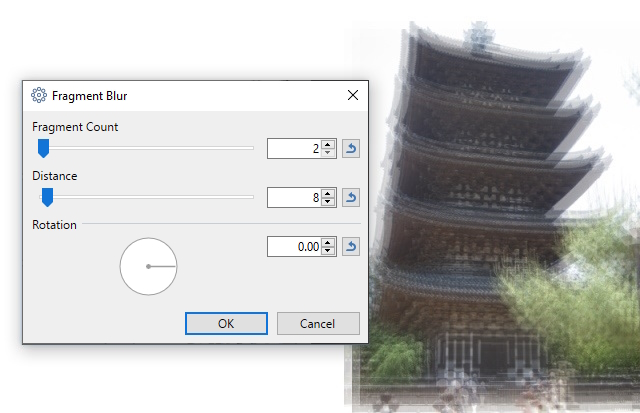
 Fragment Blur
Fragment Blur
Copies or "fragments" of the image are superimposed over the original.
The specified number of copies (
This blur can be useful when creating an unfocussed multi-viewed version of an image. The effect is not unlike modern interpretations of insect-like vision and could be used to fake "drunken" or "semi-conscious" vision.
Example - Effects > Blurs > Fragment Blur
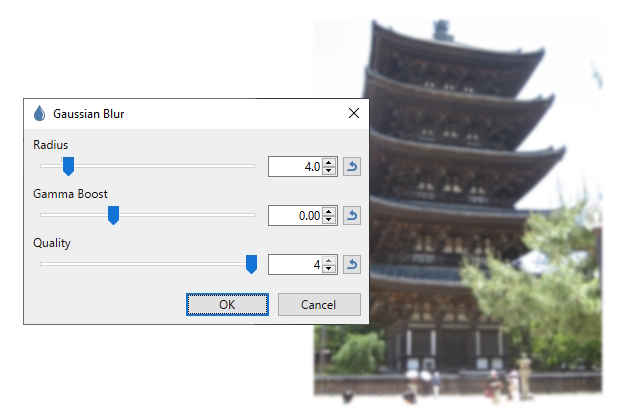
 Gaussian Blur
Gaussian Blur
This blur applies the well known Gaussian blur formula to the image. The result is a defocusing blur in it's simplest sense.
Example - Effects > Blurs > Gaussian Blur
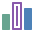 Median Blur
Median Blur
Example - Effects > Blurs > Median Blur
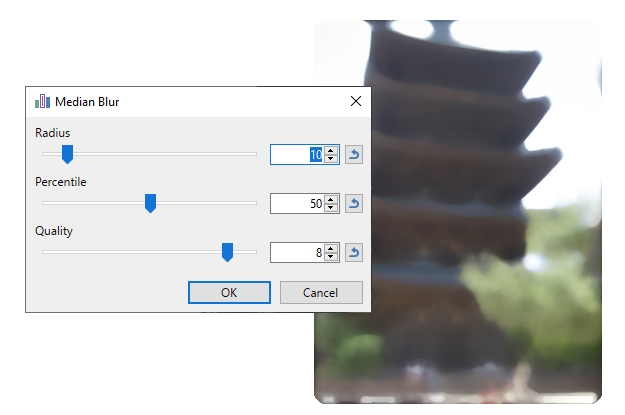
 Motion Blur
Motion Blur
This effect is useful for adding an illusion of motion to an image, as if a photograph had been taken while the subject was moving across the frame.
The
The
Example - Effects > Blurs > Motion Blur
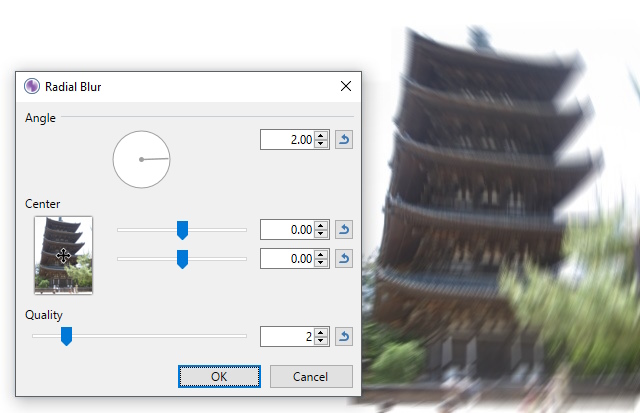
 Radial Blur
Radial Blur
This effect is similar to
The
Example - Effects > Blurs > Radial Blur
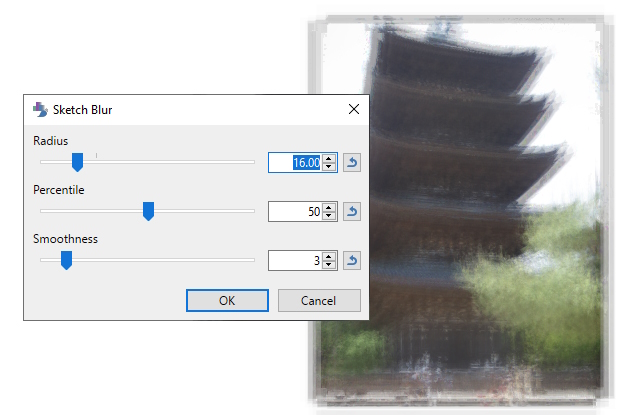
 Sketch Blur
Sketch Blur
Sketch Blur is a new blur effect unique to Paint.NET. It was adapted from Andrey Akinshin's implementation of the P² Quantile Estimator algorithm, which is used to calculate an approximation of the median for a stream of values. You can think of this algorithm as taking a Monte Carlo approach to calculating a median.
The effect produces an artistic effect like a coarse-grained brush stroke painting.
Example - Effects > Blurs > Sketch Blur
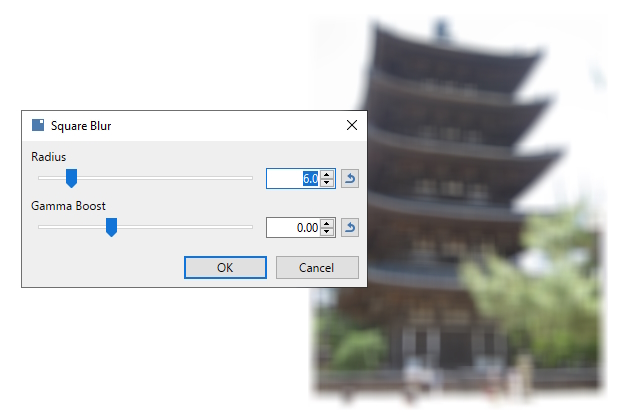
 Square Blur
Square Blur
This simple blur effect computes the average color of the surrounding square area. This effect could be considered a very high-performance, but very inaccurate approximation, of the Bokeh Blur effect (which averages out the surrounding circular area).
The
Example - Effects > Blurs > Square Blur
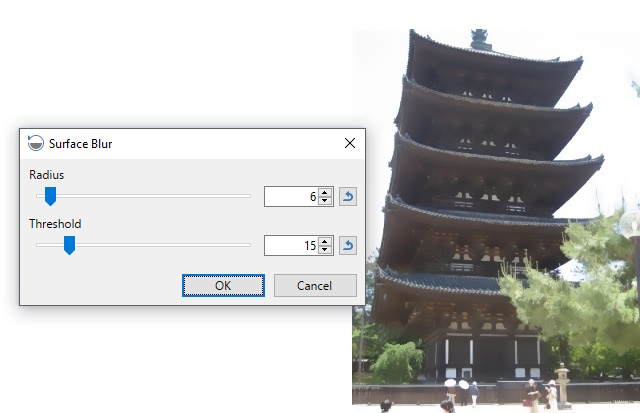
 Surface Blur
Surface Blur
This effect is used to reduce soft details or noise in an image while retaining most edge details and contrast. The result is a cleaner, simplified version of the original.
The
Example - Effects > Blurs > Surface Blur
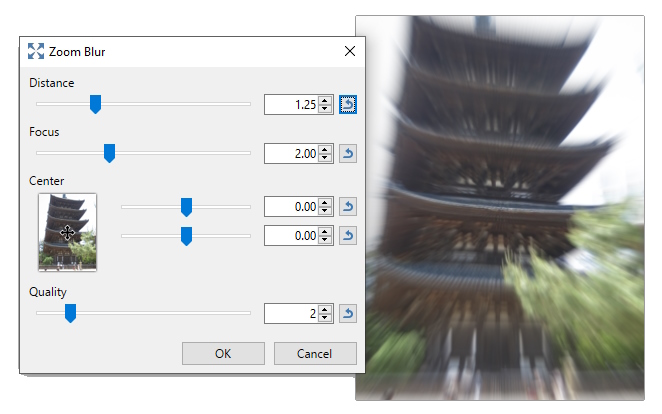
 Zoom Blur
Zoom Blur
This effect gives the appearance of motion towards the image subject. The effect effectively mimics blurring in the 3rd dimension as if the viewer was rapidly closing in on the focal point.
Another way of looking at this effect is that it is
The
Example - Effects > Blurs > Zoom Blur